Tyk Data Plane Chart
Last updated:
The tyk-data-plane chart provides the default deployment of a Tyk data plane for Tyk Self Managed MDCB or Tyk Cloud users. It will deploy the data plane components that remotely connect to a MDCB control plane.
What components are deployed with Tyk Data Plane Chart?
It includes the following components:
- Tyk Gateway: An open source Enterprise API Gateway, supporting REST, GraphQL, TCP and gRPC protocols.
- Tyk Pump: An analytics purger that moves the data generated by your Tyk gateways to any back-end storage.
Furthermore, it has all the required modifications to easily connect to Tyk Cloud or Multi Data Center (MDCB) control plane.
By default, this chart installs following components as subcharts on a Kubernetes cluster using the Helm package manager.
| Component | Enabled by Default? | Flag |
|---|---|---|
| Tyk Gateway | true | n/a |
| Tyk Pump | true | global.components.pump |
To enable or disable each component, change the corresponding enabled flag.
Also, you can set the version of each component through image.tag. You can find the list of version tags available from Docker hub.
For a quick start guide, please see deploy hybrid gateway.
Prerequisites
- Kubernetes 1.19+
- Helm 3+
- Redis should already be installed or accessible by the gateway.
- Connection details to remote control plane. See below for how to obtain them from Tyk Cloud or Tyk Control Plane chart.
Obtain Remote Control Plane Connection details from Tyk Cloud
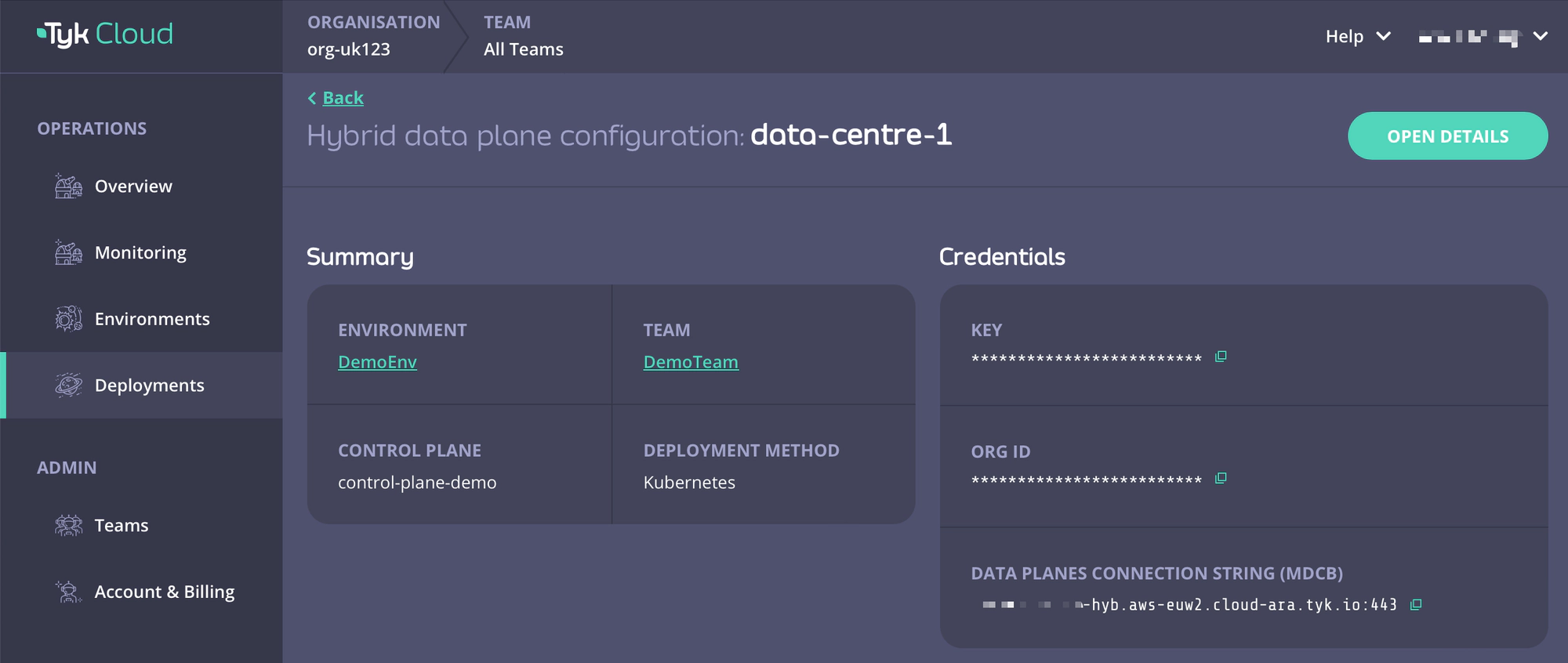
For Tyk Cloud users who want to deploy hybrid data planes, you can easily obtain your remote control plane connection details on Tyk Cloud.
- Go to Deployment tab and create a Hybrid data plane configuration. You can also select from an existing one.
- Copy Key, Org ID, and Data Planes Connection String (MDCB) as
global.remoteControlPlane’suserApiKey,orgId, andconnectionStringrespectively.
Obtain Remote Control Plane Connection Details from tyk-control-plane Chart
For Tyk Self-Managed MDCB users who want to deploy data planes, you can obtain MDCB connection details from the notes of tyk-control-plane installation output, as listed below.
=== Tyk Control Plane Details ===
Before a worker gateway that is deployed in data plane can connect to MDCB, it is important to set remote control plane options.
If the worker gateway will be deployed via Helm, tyk-data-plane chart helps to facilitate this process.
1- First obtain required connection details from Tyk MDCB:
export GROUP_ID=your_group_id # You can use any name for your group.
export USER_API_KEY=$(kubectl get secret --namespace tyk tyk-operator-conf -o jsonpath="{.data.TYK_AUTH}" | base64 --decode)
export ORG_ID=$(kubectl get secret --namespace tyk tyk-operator-conf -o jsonpath="{.data.TYK_ORG}" | base64 --decode)
2- Create a Kubernetes Secret based on credentials in data plane's namespace, e.g. `tyk-dp`.
kubectl create namespace tyk-dp
kubectl create secret generic tyk-data-plane-details \
--from-literal "orgId=$ORG_ID" \
--from-literal "userApiKey=$USER_API_KEY" \
--from-literal "groupID=$GROUP_ID" \
--namespace tyk-dp
3- Refer to this Kubernetes secret (tyk-data-plane-details) while installing worker gateways through
`global.remoteControlPlane.useSecretName` in tyk-data-plane chart.
4- Set `global.remoteControlPlane.connectionString`, `global.remoteControlPlane.useSSL` and
`global.remoteControlPlane.sslInsecureSkipVerify` in tyk-data-plane chart to access MDCB service.
If data plane is deployed in the same cluster, it can be accessed via this connection string:
export MDCB_CONNECTIONSTRING="mdcb-svc-tyk-control-plane-tyk-mdcb.tyk.svc:9091"
If data plane is not deployed in the same cluster as control plane, get the connection string according
to how MDCB service is exposed.
-
Follow installation output to export USER_API_KEY, ORG_ID, and MDCB_CONNECTIONSTRING. The values can be used to set
global.remoteControlPlane’suserApiKey,orgId, andconnectionStringrespectively. -
Also verify that the SSL connection configuration is set correctly:
global:
remoteControlPlane:
# enable/disable ssl
useSSL: false
# Disables SSL certificate verification
sslInsecureSkipVerify: true
Tyk Data Plane Chart Installations
Installing the Chart
To install the chart from the Helm repository in namespace tyk-dp with the release name tyk-data-plane, issue the following commands:
helm repo add tyk-helm https://helm.tyk.io/public/helm/charts/
helm repo update
helm show values tyk-helm/tyk-data-plane > values.yaml
For further documentation relating to helm command usage, please refer to the helm docs.
At a minimum, modify values.yaml for the following settings:
Consult the Configuration section for the available configuration options and modify your local values.yaml file accordingly. Then install the chart by issuing the following command below:
helm install tyk-data-plane tyk-helm/tyk-data-plane -n tyk-dp --create-namespace -f values.yaml
Uninstalling the Chart
helm uninstall tyk-data-plane -n tyk-dp
This removes all the Kubernetes components associated with the chart and deletes the release.
Upgrading Chart
helm upgrade tyk-data-plane tyk-helm/tyk-data-plane -n tyk-dp
Configuration
To list all configurable options with detailed comments, issue the following command:
helm show values tyk-helm/tyk-data-plane > values.yaml
You can update any value in your local values.yaml file and use -f [filename] flag to override default values during installation.
Alternatively, you can use --set flag to set it in Tyk installation.
To configure Tyk components, users can utilize both config files and environment variables. Notably, environment variables take precedence over config files. To maintain simplicity and consistency, the Tyk Helm Charts deploy components with an empty config file while setting container environment variables based on user-defined values. This approach ensures seamless integration with Kubernetes practices, allowing for efficient management of configurations. For a comprehensive overview of available configurations, please refer to the configuration documentation.
Setting Environment Variables
Should any environment variables not be set by the Helm Chart, users can easily add them under the extraEnvs section within the charts for further customization. Values set under extraEnvs would take precedence over all configurations.
Example of setting extra environment variable to gateway:
tyk-gateway:
gateway:
extraEnvs:
- name: TYK_GW_LOGLEVEL
value: debug
An example is listed below for setting extra environment variable using ConfigMap data, using gateway:
tyk-gateway:
gateway:
extraEnvs:
- name: CONFIG_USERNAME
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: backend-user
key: backend-username
An example is listed below for setting extra environment variable using secret data, using gateway:
tyk-gateway:
gateway:
extraEnvs:
- name: SECRET_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: backend-user
key: backend-username
In the above example, an extra environment variable SECRET_USERNAME will be added to the Gateway container, with a value of backend-username associated with the secret backend-user. It is useful if you want to access secret data from Tyk Gateway configuration file (tyk.conf) or API definitions.
Set Redis Connection Details (Required)
Tyk uses Redis for distributed rate-limiting and token storage. You may use the Bitnami chart to install or Tyk’s simple-redis chart for POC purpose.
Set the following values after installing Redis:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
global.redis.addrs |
Redis addresses |
global.redis.pass |
Redis password in plain text |
global.redis.passSecret.name |
If global.redis.pass is not provided, you can store it in a secret and provide the secret name here |
global.redis.passSecret.keyName |
key name to retrieve Redis password from the secret |
Recommended: via Bitnami chart
For Redis you can use these rather excellent charts provided by Bitnami. Copy the following commands to add it:
helm upgrade tyk-redis oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/redis -n tyk --create-namespace --install --version 19.0.2
Note
Please make sure you are installing Redis versions that are supported by Tyk. Please refer to Tyk docs to get list of supported versions.
Follow the notes from the installation output to get connection details and password.
Redis(TM) can be accessed on the following DNS names from within your cluster:
tyk-redis-master.tyk.svc.cluster.local for read/write operations (port 6379)
tyk-redis-replicas.tyk.svc.cluster.local for read-only operations (port 6379)
export REDIS_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace tyk tyk-redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 --decode)
The Redis address as set by Bitnami is tyk-redis-master.tyk.svc.cluster.local:6379
You can reference the password secret generated by Bitnami chart by --set global.redis.passSecret.name=tyk-redis and --set global.redis.passSecret.keyName=redis-password, or just set --set global.redis.pass=$REDIS_PASSWORD.
helm install --set global.redis.passSecret.name=tyk-redis --set global.redis.passSecret.keyName=redis-password tyk-data-plane tyk-helm/tyk-data-plane
or
export REDIS_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace tyk tyk-redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 --decode)
helm install --set global.redis.pass=$REDIS_PASSWORD tyk-data-plane tyk-helm/tyk-data-plane
Evaluation only: via simple-redis chart
Another option for Redis, to get started quickly, is to use our simple-redis chart.
Warning
Please note that these provided charts must never be used in production or for anything but a quick start evaluation only. Use Bitnami Redis or Official Redis installation guides in any other case. We provide this chart, so you can quickly deploy Tyk gateway, but it is not meant for long term storage of data.
helm install redis tyk-helm/simple-redis -n tyk
The Tyk Helm Chart can connect to simple-redis in the same namespace by default. You do not need to set Redis address and password in values.yaml.
Protect Confidential Fields with Kubernetes Secrets
In the values.yaml file, some fields are considered confidential, such as APISecret, connection strings, etc.
Declaring values for such fields as plain text might not be desired for all use cases. Instead, for certain fields, Kubernetes secrets can be referenced, and the chart will define container environment variables using secret data.
This section describes how to use Kubernetes secrets to declare confidential fields.
APISecret
The global.secrets.APISecret field configures a header value used in every interaction with Tyk Gateway API.
It can be configured via global.secrets.APISecret as a plain text or Kubernetes secret which includes APISecret key in it. Then, this secret must be referenced via global.secrets.useSecretName.
global:
secrets:
APISecret: CHANGEME
useSecretName: "mysecret" # where mysecret includes `APISecret` key with the desired value.
Remote Control Plane Configuration
All configurations regarding remote control plane (orgId, userApiKey, and groupID) can be set via
Kubernetes secret.
Instead of explicitly setting them in the values file, just create a Kubernetes secret including orgId, userApiKey and groupID keys and refer to it in global.remoteControlPlane.useSecretName.
- Create a secret that contains
orgId,userApiKeyandgroupIDkeys in it:
kubectl create secret generic foo-secret -n tyk --from-literal=orgId=[ORGID] --from-literal=userApiKey=[APIKEY]--from-literal=groupID=[GROUPID]
- Refer to it in
global.remoteControlPlane.useSecretName.
global:
remoteControlPlane:
useSecretName: "foo-secret"
Redis Password
The Redis password can also be provided via a secret. Store Redis password in Kubernetes secret and refer to this secret
via global.redis.passSecret.name and global.redis.passSecret.keyName field, as follows:
global:
redis:
passSecret:
name: "yourSecret"
keyName: "redisPassKey"
Tyk MDCB Synchroniser (Optional)
If control plane MDCB has enabled Synchroniser feature, the following fields should be set accordingly:
global:
mdcbSynchronizer:
enabled: true
keySpaceSyncInterval: 10
Gateway Configurations
Configure below inside tyk-gateway section.
Update Tyk Gateway Version
Set version of gateway at tyk-gateway.gateway.image.tag. You can find the list of version tags available from Docker hub. Please check Tyk Release notes carefully while upgrading or downgrading.
Enabling TLS
Enable TLS
We have provided an easy way to enable TLS via the global.tls.gateway flag. Setting this value to true will
automatically enable TLS using the certificate provided under tyk-gateway/certs/.
Configure TLS secret
If you want to use your own key/cert pair, please follow the following steps:
- Create a TLS secret using your cert and key pair.
- Set
global.tls.gatewayto true. - Set
tyk-gateway.gateway.tls.useDefaultTykCertificateto false. - Set
tyk-gateway.gateway.tls.secretNameto the name of the newly created secret.
Add Custom CA Certificates
To add your custom Certificate Authority(CA) to your containers, you can mount your CA certificate directly into /etc/ssl/certs folder.
extraVolumes:
- name: self-signed-ca
secret:
secretName: self-signed-ca-secret
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: self-signed-ca
mountPath: "/etc/ssl/certs/myCA.pem"
subPath: myCA.pem
Enabling gateway autoscaling
You can enable autoscaling of the gateway by --set tyk-gateway.gateway.autoscaling.enabled=true. By default, it will enable the Horizontal Pod Autoscaler resource with target average CPU utilization at 60%, scaling between 1 and 3 instances. To customize those values you can modify the tyk-gateway section of values.yaml as shown below:
tyk-gateway:
gateway:
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 3
maxReplicas: 30
Built-in rules include tyk-gateway.gateway.autoscaling.averageCpuUtilization for CPU utilization (set by default at 60%) and tyk-gateway.gateway.autoscaling.averageMemoryUtilization for memory (disabled by default). In addition to that you can define rules for custom metrics using tyk-gateway.gateway.autoscaling.autoscalingTemplate list:
tyk-gateway:
gateway:
autoscaling:
autoscalingTemplate:
- type: Pods
pods:
metric:
name: nginx_ingress_controller_nginx_process_requests_total
target:
type: AverageValue
averageValue: 10000m
Accessing Gateway
Service port
Default service port of gateway is 8080. You can change this at global.servicePorts.gateway.
Ingress
An Ingress resource is created if tyk-gateway.gateway.ingress.enabled is set to true.
ingress:
# if enabled, creates an ingress resource for the gateway
enabled: true
# specify ingress controller class name
className: ""
# annotations for ingress
annotations: {}
# ingress rules
hosts:
- host: tyk-gw.local
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# tls configuration for ingress
# - secretName: chart-example-tls
# hosts:
# - chart-example.local
tls: []
Control Port
Set tyk-gateway.gateway.control.enabled to true will allow you to run the Gateway API on a separate port and protect it behind a firewall if needed.
Sharding
Configure the gateways to load APIs with specific tags only by enabling tyk-gateway.gateway.sharding.enabled, and set tags to comma separated lists of matching tags.
# Sharding gateway allows you to selectively load APIs to specific gateways.
# If enabled make sure you have at least one gateway that is not sharded.
# Also be sure to match API segmentation tags with the tags selected below.
sharding:
enabled: true
tags: "edge,dc1,product"
OpenTelemetry
To enable OpenTelemetry for Gateway set gateway.opentelemetry.enabled flag to true. It is disabled by default.
You can also configure connection settings for it’s exporter. By default grpc exporter is enabled on localhost:4317 endpoint.
To enable TLS settings for the exporter, you can set gateway.opentelemetry.tls.enabled to true.
Liveness and readiness probes
Gateway liveness probes can be customised via gateway.livenessProbe field. All fields from PodLivenessProbe object can be added here. If set to empty or nil, the default health check on /health will be performed.
Gateway readiness probes can be customised via gateway.readinessProbe field. All fields from PodReadinessProbe object can be added here. If set to empty or nil, the default health check on /health will be performed.
For further details for configuring Tyk Gateway, please consult the Tyk Gateway Configuration Options guide.
Pump Configurations
To enable Pump, set global.components.pump to true, and configure as detailed below inside tyk-pump section.
| Pump | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Prometheus Pump (Default) | Add prometheus to tyk-pump.pump.backend, and add connection details for prometheus under tyk-pump.pump.prometheusPump. |
| Hybrid Pump (Default) | Add hybrid to tyk-pump.pump.backend, and add remoteControlPlane details under global.remoteControlPlane. |
| Other Pumps | Add the required environment variables in tyk-pump.pump.extraEnvs |
Prometheus Pump
Add prometheus to tyk-pump.pump.backend, and add connection details for prometheus under tyk-pump.pump.prometheusPump.
We also support monitoring using Prometheus Operator. All you have to do is set tyk-pump.pump.prometheusPump.prometheusOperator.enabled to true.
This will create a PodMonitor resource for your Pump instance.
Hybrid Pump
Add hybrid to tyk-pump.pump.backend, and add remoteControlPlane details under global.remoteControlPlane.
# Set remoteControlPlane connection details if you want to configure hybrid pump.
remoteControlPlane:
# connection string used to connect to an MDCB deployment. For Tyk Cloud users, you can get it from Tyk Cloud Console and retrieve the MDCB connection string.
connectionString: ""
# orgID of your dashboard user
orgId: ""
# API key of your dashboard user
userApiKey: ""
# needed in case you want to have multiple data-planes connected to the same redis instance
groupID: ""
# enable/disable ssl
useSSL: true
# Disables SSL certificate verification
sslInsecureSkipVerify: true
# hybridPump configures Tyk Pump to forward Tyk metrics to a Tyk Control Plane.
# Please add "hybrid" to .Values.pump.backend in order to enable Hybrid Pump.
hybridPump:
# Specify the frequency of the aggregation in minutes or simply turn it on by setting it to true
enableAggregateAnalytics: true
# Hybrid pump RPC calls timeout in seconds.
callTimeout: 10
# Hybrid pump connection pool size.
poolSize: 5
Other Pumps
To setup other backends for Pump, refer to this document and add the required environment variables in tyk-pump.pump.extraEnvs