Tyk Self-Managed
What is Tyk On-Premises / Self-Managed ?
Tyk Self-Managed is the easiest way to install our Full Lifecycle API Management solution in your own infrastructure. There is no calling home, and there are no usage limits. You have full control. Sign up for a free trial to test it out:
Installing Tyk Self-Managed:
Please visit our Self-Managed installation page to get started.
Licencing
Read more about licensing here.
Tyk Components
The full Tyk Self-Managed system consists of:
- Tyk Gateway: Tyk Gateway is provided ‘Batteries-included’, with no feature lockout. It is an open source enterprise API Gateway, supporting REST, GraphQL, TCP and gRPC protocols, that protects, secures and processes your APIs.
- Tyk Dashboard: The management Dashboard and integration API manage a cluster of Tyk Gateways and also show analytics and features of the Developer portal. The Dashboard also provides the API Developer Portal, a customisable developer portal for your API documentation, developer auto-enrolment and usage tracking.
- Tyk Pump: Tyk Pump handles moving analytics data between your gateways and your Dashboard (amongst other data sinks). The Tyk Pump is an open source analytics purger that moves the data generated by your Tyk nodes to any back-end.
- Tyk Identity Broker (Optional): Tyk Identify Broker handles integrations with third-party IDP’s. It (TIB) is a component providing a bridge between various Identity Management Systems such as LDAP, Social OAuth (e.g. GPlus, Twitter, GitHub) or Basic Authentication providers, to your Tyk installation.
- Tyk Multi-Data Center Bridge (Optional, add-on): Tyk Multi-Data Center Bridge allows for the configuration of a Tyk ecosystem that spans many data centers and clouds. It also (MDCB) acts as a broker between Tyk Gateway Instances that are isolated from one another and typically have their own Redis DB.
Architecture
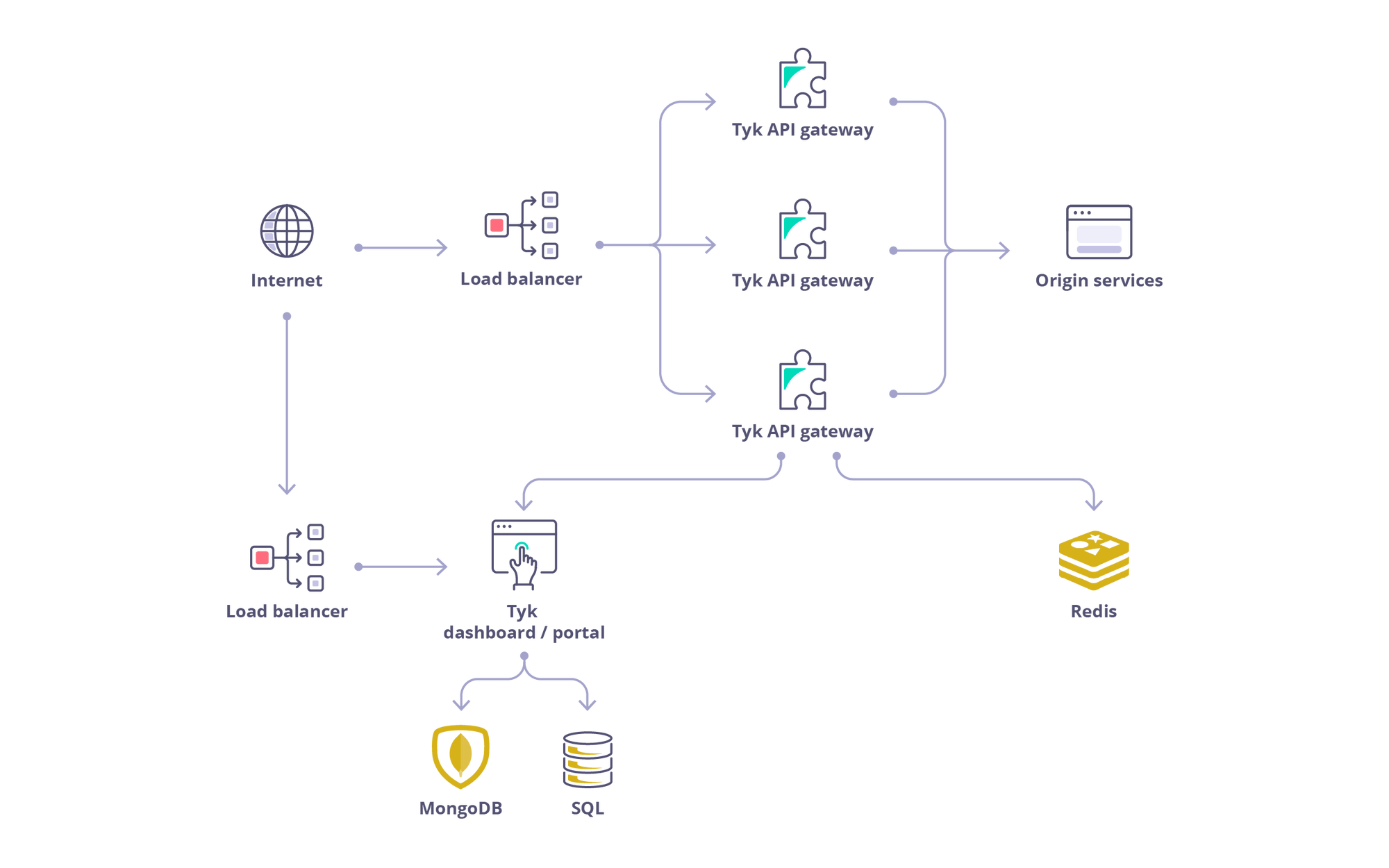
Dependencies & Database Support
Tyk Dashboard
By default the Tyk Dashboard uses MongoDB. You can use the following as a drop-in replacement:
- DocumentDB
- Azure Cosmos DB version 3.2
- MongoDB 3.x and 4.0.x
- From v4.0, we have added SQL support. In a production environment, we support the following PostgreSQL versions:
13.3, 12.7, 11.12, 10.17, 9.6.22
Note
If you are using DocumentDB, capped collections are not supported. See here for more details.
- MongoDB 3.x and 4.0.x
- MongoDB Cloud / AtlasDB
In order to integrate with AtlasDB, make sure the IP firewall connections are whitelisted on the Atlas side, and then use the following Tyk Dashboard configurations to connect:
- TYK_DB_MONGOURL=mongodb://admin:password@tykdb-shard-00-00.h42pp.mongodb.net:27017,tykdb-shard-00-01.h42pp.mongodb.net:27017,tykdb-shard-00-02.h42pp.mongodb.net:27017/tyk_analytics?authSource=admin
- TYK_DB_ENABLECLUSTER=false
- TYK_DB_MONGOUSESSL=true
More information on these configuration variables here.
Tyk Gateway
Visit the Gateway page for more info.
- Redis 2.8.x to 5.0.x
Init Systems
Tyk packages support systemd, Upstart (both 0.6.x and 1.x) and SysVinit Linux init systems. During package installation only one is chosen depending on the operating system support, e.g.:
- CentOS 6, RHEL 6, Amazon Linux ship with Upstart 0.6.x
- Ubuntu 14.04, Debian Jessie with Upstart 1.x
- CentOS 7, RHEL 7, Ubuntu 16.04, Debian Stretch are running with systemd
- Certain older distros may only provide SysVinit but all of them typically provide compatibility with its scripts
Note that any init scripts of your choosing can be used instead of automatically detected ones by copying them from the install/inits directory inside the package directory.
This init system variance implies there are different ways to manage the services and collect service logs.
Upstart
For Upstart, service management can be performed through the initctl or a set of start, stop, restart and status commands. Upstart 1.x also works with the service command.
systemd
For systemd, either systemctl or service commands may be utilised.
The service command can usually be used with SysVinit scripts, as well as invoking them directly.
Service logs availability
- Upstart 0.6.x and SysVinit: log files are located in
/var/logsfor every respective service, e.g./var/logs/tyk-gateway.stderrand/var/logs/tyk-gateway.stdout - Upstart 1.x: by default everything is stored in
/var/logs/upstartdirectory, e.g./var/logs/upstart/tyk-gateway.log - systemd utilises its own logging mechanism called journald, which is usable via the
journalctlcommand, e.g.journalctl -u tyk-gateway
Please consult with respective init system documentation for more details on how to use and configure it.
