Create Custom Authentication Plugin with .NET
Introduction
This tutorial will guide you through the creation of a custom authentication plugin for Tyk with a gRPC based plugin with .NET and C#.
For additional information about gRPC, check the official documentation here.
Requirements
- Tyk Gateway: This can be installed using standard package management tools like Yum or APT, or from source code. See here for more installation options.
- The Tyk CLI utility, which is bundled with our RPM and DEB packages, and can be installed separately from https://github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk-cli
- In Tyk 2.8 the Tyk CLI is part of the gateway binary, you can find more information by running “tyk help bundle”.
- .NET Core for your OS: https://www.microsoft.com/net/core
- gRPC tools: https://grpc.io/docs/quickstart/csharp.html#generate-grpc-code
What is gRPC?
gRPC is a very powerful framework for RPC communication across different languages. It was created by Google and makes heavy use of HTTP2 capabilities and the Protocol Buffers serialization mechanism.
Why Use it for Plugins?
When it comes to built-in plugins, we have been able to integrate several languages like Python, Javascript & Lua in a native way: this means the middleware you write using any of these languages runs in the same process. For supporting additional languages we have decided to integrate gRPC connections and perform the middleware operations outside of the Tyk process. The flow of this approach is as follows:
- Tyk receives a HTTP request.
- Your gRPC server performs the middleware operations (for example, any modification of the request object).
- Your gRPC server sends the request back to Tyk.
- Tyk proxies the request to your upstream API.
The sample code that we’ll use implements a very simple authentication layer using .NET and the proper gRPC bindings generated from our Protocol Buffers definition files.

Create the Plugin
Setting up the .NET Project
We use the .NET CLI tool to generate the initial files for our project:
cd ~
dotnet new console -o tyk-plugin
We now have a tyk-plugin directory containing the basic skeleton of a .NET application.
From the tyk-plugin directory we need to install a few packages that the gRPC server requires:
dotnet add package Grpc --version 1.6.0
dotnet add package System.Threading.ThreadPool --version 4.3.0
dotnet add package Google.Protobuf --version 3.4.0
- The
Grpcpackage provides base code for our server implementation. - The
ThreadPoolpackage is used byGrpc. - The
Protobufpackage will be used by our gRPC bindings.
gRPC Tools and Bindings Generation
We need to install the gRPC tools to generate the bindings. We recommended you follow the official guide here: https://grpc.io/docs/quickstart/csharp.html#generate-grpc-code.
Run the following Commands (both MacOS and Linux)
cd ~/tyk-plugin
temp_dir=packages/Grpc.Tools.1.6.x/tmp
curl_url=https://www.nuget.org/api/v2/package/Grpc.Tools/
mkdir -p $temp_dir && cd $temp_dir && curl -sL $curl_url > tmp.zip; unzip tmp.zip && cd .. && cp -r tmp/tools . && rm -rf tmp && cd ../..
chmod -Rf +x packages/Grpc.Tools.1.6.x/tools/
Then run the following, depending on your OS:
MacOS (x64)
export GRPC_TOOLS=packages/Grpc.Tools.1.6.x/tools/macosx_x64
Linux (x64)
export GRPC_TOOLS=packages/Grpc.Tools.1.6.x/tools/linux_x64
The GRPC_TOOLS environment variable will point to the appropriate GrpcTools path that matches our operating system and architecture. The last step is to export a variable for the protoc program; this is the main program used to generate bindings:
export GRPC_PROTOC=$GRPC_TOOLS/protoc
Now that we can safely run protoc, we can download the Tyk Protocol Buffers definition files. These files contain the data structures used by Tyk. See Data Structures for more information:
cd ~/tyk-plugin
git clone https://github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk-protobuf
To generate the bindings, we create an empty directory and run the protoc tool using the environment variable that was set before:
mkdir Coprocess
$GRPC_PROTOC -I=tyk-protobuf/proto --csharp_out=Coprocess --grpc_out=Coprocess --plugin=protoc-gen-grpc=$GRPC_TOOLS/grpc_csharp_plugin tyk-protobuf/proto/*.proto
Run the following command to check the binding directory:
ls Coprocess
The output will look like this:
CoprocessCommon.cs CoprocessObject.cs CoprocessReturnOverrides.cs
CoprocessMiniRequestObject.cs CoprocessObjectGrpc.cs CoprocessSessionState.cs
Server Implementation
Create a file called Server.cs.
Add the following code to Server.cs.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Grpc.Core;
using Coprocess;
class DispatcherImpl : Dispatcher.DispatcherBase
{
public DispatcherImpl()
{
Console.WriteLine("Instantiating DispatcherImpl");
}
// The Dispatch method will be called by Tyk for every configured hook, we'll implement a very simple dispatcher here:
public override Task<Coprocess.Object> Dispatch(Coprocess.Object thisObject, ServerCallContext context)
{
// thisObject is the request object:
Console.WriteLine("Receiving object: " + thisObject.ToString());
// hook contains the hook name, this will be defined in our plugin bundle and the implementation will be a method in this class (DispatcherImpl), we'll look it up:
var hook = this.GetType().GetMethod(thisObject.HookName);
// If hook is null then a handler method for this hook isn't implemented, we'll log this anyway:
if (hook == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hook name: " + thisObject.HookName + " (not implemented!)");
// We return the unmodified request object, so that Tyk can proxy this in the normal way.
return Task.FromResult(thisObject);
};
// If there's a handler method, let's log it and proceed with our dispatch work:
Console.WriteLine("Hook name: " + thisObject.HookName + " (implemented)");
// This will dynamically invoke our hook method, and cast the returned object to the required Protocol Buffers data structure:
var output = hook.Invoke(this, new object[] { thisObject, context });
return (Task<Coprocess.Object>)output;
}
// MyPreMiddleware implements a PRE hook, it will be called before the request is proxied upstream and before the authentication step:
public Task<Coprocess.Object> MyPreMiddleware(Coprocess.Object thisObject, ServerCallContext context)
{
Console.WriteLine("Calling MyPreMiddleware.");
// We'll inject a header in this request:
thisObject.Request.SetHeaders["my-header"] = "my-value";
return Task.FromResult(thisObject);
}
// MyAuthCheck implements a custom authentication mechanism, it will initialize a session object if the token matches a certain value:
public Task<Coprocess.Object> MyAuthCheck(Coprocess.Object thisObject, ServerCallContext context)
{
// Request.Headers contains all the request headers, we retrieve the authorization token:
var token = thisObject.Request.Headers["Authorization"];
Console.WriteLine("Calling MyAuthCheck with token = " + token);
// We initialize a session object if the token matches "abc123":
if (token == "abc123")
{
Console.WriteLine("Successful auth!");
var session = new Coprocess.SessionState();
session.Rate = 1000;
session.Per = 10;
session.QuotaMax = 60;
session.QuotaRenews = 1479033599;
session.QuotaRemaining = 0;
session.QuotaRenewalRate = 120;
session.Expires = 1479033599;
session.LastUpdated = 1478033599.ToString();
thisObject.Metadata["token"] = token;
thisObject.Session = session;
return Task.FromResult(thisObject);
}
// If the token isn't "abc123", we return the request object in the original state, without a session object, Tyk will reject this request:
Console.WriteLine("Rejecting auth!");
return Task.FromResult(thisObject);
}
}
Create a file called Program.cs to instantiate our dispatcher implementation and start a gRPC server.
Add the following code to Program.cs.
using System;
using Grpc.Core;
namespace tyk_plugin
{
class Program
{
// Port to attach the gRPC server to:
const int Port = 5555;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// We initialize a Grpc.Core.Server and attach our dispatcher implementation to it:
Server server = new Server
{
Services = { Coprocess.Dispatcher.BindService(new DispatcherImpl()) },
Ports = { new ServerPort("localhost", Port, ServerCredentials.Insecure) }
};
server.Start();
Console.WriteLine("gRPC server listening on " + Port);
Console.WriteLine("Press any key to stop the server...");
Console.ReadKey();
server.ShutdownAsync().Wait();
}
}
}
To run the gRPC server use the following command from the plugin directory:
dotnet run
The gRPC server will listen on port 5555 (as defined in Program.cs). In the next steps we’ll setup the plugin bundle and modify Tyk to connect to our gRPC server.
Setting up the Plugin Bundle
We need to create a manifest file within the tyk-plugin directory. This file contains information about our plugin and how we expect it to interact with the API that will load it. This file should be named manifest.json and needs to contain the following:
{
"custom_middleware": {
"driver": "grpc",
"auth_check": {
"name": "MyAuthMiddleware",
"path": "",
"raw_body_only": false,
"require_session": false
}
}
}
- The
custom_middlewareblock contains the middleware settings like the plugin driver we want to use (driver) and the hooks that our plugin will expose. We use theauth_checkhook for this tutorial. For other hooks see here. - The
namefield references the name of the function that we implement in our plugin code -MyAuthMiddleware. This will be handled by our dispatcher gRPC method (implemented inServer.cs). - The
pathfield is the path to the middleware component. - The
raw_body_onlyfield - The
require_sessionfield, if set totruegives you access to the session object. It will be supplied as a session variable to your middleware processor function
To bundle our plugin run the following command in the tyk-plugin directory. Check your tyk-cli install path first:
/opt/tyk-gateway/utils/tyk-cli bundle build -y
From Tyk v2.8 upwards you can use:
/opt/tyk-gateway/bin/tyk bundle build -y
A plugin bundle is a packaged version of the plugin. It may also contain a cryptographic signature of its contents. The -y flag tells the Tyk CLI tool to skip the signing process in order to simplify the flow of this tutorial.
For more information on the Tyk CLI tool, see here.
You should now have a bundle.zip file in the tyk-plugin directory.
Publish the Plugin
To publish the plugin, copy or upload bundle.zip to a local web server like Nginx, or Apache or storage like Amazon S3. For this tutorial we’ll assume you have a web server listening on localhost and accessible through http://localhost.
Configure Tyk
You will need to modify the Tyk global configuration file tyk.conf to use gRPC plugins. The following block should be present in this file:
"coprocess_options": {
"enable_coprocess": true,
"coprocess_grpc_server": "tcp://localhost:5555"
},
"enable_bundle_downloader": true,
"bundle_base_url": "http://localhost/bundles/",
"public_key_path": ""
tyk.conf Options
enable_coprocess: This enables the plugin.coprocess_grpc_server: This is the URL of our gRPC server.enable_bundle_downloader: This enables the bundle downloader.bundle_base_url: This is a base URL that will be used to download the bundle. You should replace the bundle_base_url with the appropriate URL of the web server that’s serving your plugin bundles. For now HTTP and HTTPS are supported but we plan to add more options in the future (like pulling directly from S3 buckets).public_key_path: Modifypublic_key_pathin case you want to enforce the cryptographic check of the plugin bundle signatures. If thepublic_key_pathisn’t set, the verification process will be skipped and unsigned plugin bundles will be loaded normally.
Configure an API Definition
There are two important parameters that we need to add or modify in the API definition.
The first one is custom_middleware_bundle which must match the name of the plugin bundle file. If we keep this with the default name that the Tyk CLI tool uses, it will be bundle.zip:
"custom_middleware_bundle": "bundle.zip"
Assuming the bundle_base_url is http://localhost/bundles/, Tyk will use the following URL to download our file:
http://localhost/bundles/bundle.zip
The second parameter is specific to this tutorial, and should be used in combination with use_keyless to allow an API to authenticate against our plugin:
"use_keyless": false,
"enable_coprocess_auth": true
enable_coprocess_auth will instruct the Tyk gateway to authenticate this API using the associated custom authentication function that’s implemented by our plugin.
Configuration via the Tyk Dashboard
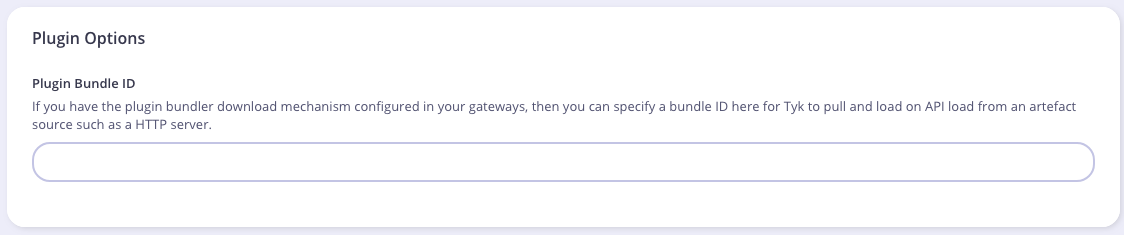
To attach the plugin to an API, from the Advanced Options tab in the API Designer enter bundle.zip in the Plugin Bundle ID field.
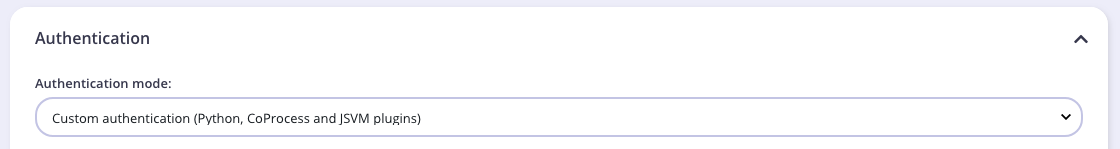
We also need to modify the authentication mechanism that’s used by the API. From the Core Settings tab in the API Designer select Use Custom Authentication (Python, CoProcess, and JSVM plugins) from the Target Details - Authentication Mode drop-down list.
Testing the Plugin
At this point we have our test HTTP server ready to serve the plugin bundle and the configuration with all the required parameters. The final step is to start or restart the Tyk Gateway (this may vary depending on how you set up Tyk):
service tyk-gateway start
A simple CURL request will be enough for testing our custom authentication middleware.
This request will trigger an authentication error:
curl http://localhost:8080/my-api/my-path -H 'Authorization: badtoken'
This will trigger a successful authentication. We’re using the token that’s specified in our server implementation (see line 57 in Server.cs):
curl http://localhost:8080/my-api/my-path -H 'Authorization: abc123'
We also have a GitHub repository that includes tests and authentication middleware.
What’s Next?
In this tutorial we learned how Tyk gRPC plugins work. For a production-level setup we suggest the following:
- Configure an appropriate web server and path to serve your plugin bundles.
- See the following GitHub repo for a gRPC based .NET plugin that incorporates authentication based on Microsoft SQL Server.
