Bearer Tokens
What is a bearer token ?
Any party in possession of a bearer token (a “bearer”) can use it to get access to the associated resources (without demonstrating possession of a cryptographic key). To prevent misuse, bearer tokens need to be protected from disclosure in storage and in transport.
Tyk provides bearer token access as one of the most convenient building blocks for managing security to your API. In a Tyk setup, this is called “Access Tokens” and is the default mode of any API Definition created for Tyk.
Bearer tokens are added to a request as a header or as a query parameter. If added as a header, they may be preceded by the word “Bearer” to indicate their type, though this is optional.
Traditionally these tokens are used as part of the Authorization header.
Enable bearer tokens in your API Definition with the Dashboard
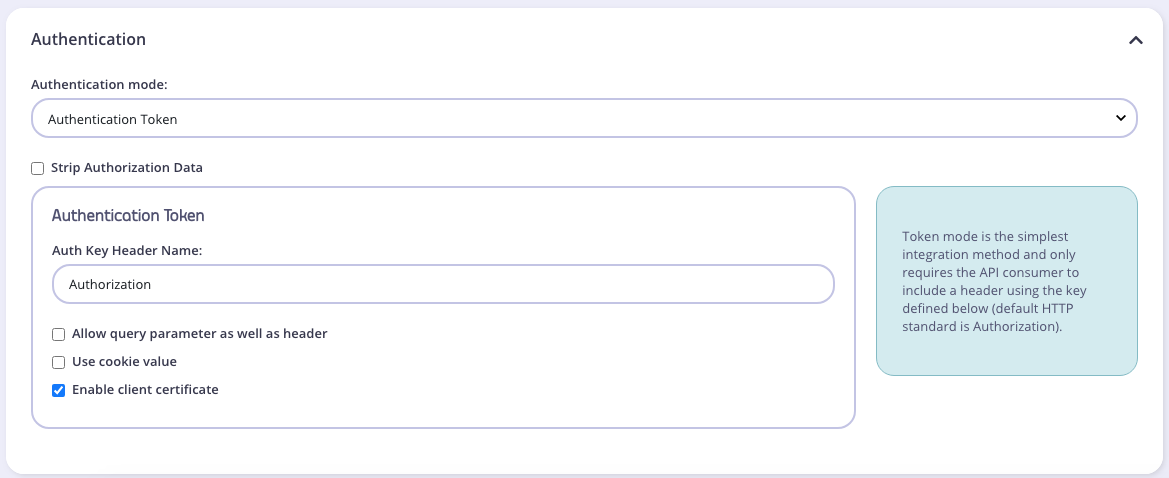
To enable the use of a bearer token in your API:
- Select your API from the System Management > APIs menu
- Scroll to the Authentication options
- Select Authentication Token from the drop-down list
- Select Strip Authorization Data to strip any authorization data from your API requests
- Tyk will by default assume you are using the
Authorizationheader, but you can change this by setting the Auth Key Header name value - You can select whether to use a URL query string parameter as well as a header, and what parameter to use. If this is left blank, it will use the Auth Key Header name value.
- You can select whether to use a cookie value. If this is left blank, it will use the Header name value.
- You can select to use a client certificate. This allows you to create dynamic keys based on certificates.
Enable bearer tokens in your API Definition with file-based
Tyk will by default use the bearer token method to protect your API unless it is told otherwise.
These tokens can be set as a header, url parameter, or cookie name of a request. A request for a resource at the API endpoint of /api/widgets/12345 that uses access tokens will require the addition of a header field, traditionally this is the Authorization header.
The name of the key can be defined as part of the API definition under the auth section of an API Definition file:
"auth": {
"auth_header_name": "authorization",
"use_param": false,
"param_name": "",
"use_cookie": false,
"cookie_name": ""
},
To use URL query parameters instead of a header, set the auth.use_param setting in your API definition to true.
Note
Unlike headers, URL query parameters are case sensitive.
To use a cookie name instead of a header or request parameter, set the use_cookie parameter to true. Cookie names are also case sensitive.
Signature validation
If you are migrating from platforms like Mashery, which use request signing, you can enable signature validation like this:
...
"auth": {
"validate_signature": true,
"signature": {
"algorithm": "MasherySHA256",
"header": "X-Signature",
"secret": "secret",
"allowed_clock_skew": 2
}
}
...
validate_signature: boolean value to tell Tyk whether to enable signature validation or not
signature.algorithm: the algorithm you wish to validate the signature against. Currently supported
MasherySHA256MasheryMD5
signature.header: header key of attempted signature
signature.secret: the shared secret which was used to sign the request
- Can hold a dynamic value, by referencing
$tyk_metaor$tyk_contextvariables. - Example:
"secret": "$tyk_meta.individual_secret". Which effectively means that you have created/imported the api key into Tyk, and have stored the shared secret in the fieldindividual_secretof the session token’s meta-data.
signature.allowed_clock_skew: allowed deviation in seconds between UNIX timestamp of Tyk & UNIX timestamp used to generate the signed request
Custom tokens
It is possible to provide Tyk with your own custom tokens, this can be achieved using the Tyk Gateway REST API. This is very useful if you have your own identity provider and don’t want Tyk to create and manage tokens for you, and instead just mirror those tokens within Tyk to off-load access control, quotas and rate limiting from your own application.
