Golang plugins
Last updated: 24 minutes read.
This is an advanced guide to help you understand more in-depth concepts behind Golang plugins.
For a quick-start guide, start here
We will look at:
- Some simple examples to see how to customise and extend Tyk with Golang plugins
- Look at some code to get some ideas as to where to go next
- Follow the process of how to build a Golang plugin and get it loaded by Tyk
Golang plugins are a very flexible and powerful way to extend the functionality of Tyk. It is based on utilising the native Golang plugins API (see https://golang.org/pkg/plugin for more details).
Every HTTP request (to your API, protected and managed by Tyk) gets passed through a chain of built-in middleware inside Tyk. This middleware performs tasks like authentication, rate limiting, white or black listing and many others - it depends on the particular API specification. In other words, the chain of middlewares is specific to an API and gets created at API re-load time. Golang plugins allow developers to create custom middleware in Golang and then add them to the chain of middleware using dedicated hooks. So when Tyk Gateway performs an API re-load it also loads the custom middleware and “injects” them into a chain to be called at different stages of the HTTP request life cycle.
It’s also possible to access the API definition data structure from within a plugin, this functionality is described in Accessing API definition from a plugin.
Plugin development flow
Initialising the gateway has slightly changed over time. In this section, you will find instructions for initializing the gateway for different versions of Tyk Gateway, before v5.1 and 5.1 onwards. Please ensure that you follow the correct section based on your Gateway version. The general steps for initialising plugins can be summarised as follows:
- Create a new folder.
- Initialise a Go module for your plugin from within the new folder.
- Determine the commit hash for the Tyk Gateway version that will be used to build the plugin. Commit hashes can be found for tagged Gateway releases.
Initialise plugin for Gateway v5.1 and above (v5.1+)
If you are using Gateway version 5.1 or higher, please follow the steps outlined in this section. These instructions are tailored to the latest Gateway software.
In Gateway version 5.1, the Gateway and plugins transitioned to using Go modules builds and don’t use Go mod vendor anymore.
The example below shows the set of commands for initialising a plugin for compatibility with Tyk Gateway 5.1.2.
mkdir tyk-plugin
cd tyk-plugin
go mod init tyk-plugin
go get github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk@ffa83a27d3bf793aa27e5f6e4c7106106286699d
go mod tidy
In the example above notice that the commit hash was used for Tyk Gateway 5.1.2
Initialise plugin for Gateway versions earlier than 5.1
For Tyk Gateway versions earlier than v5.1 you need to use go mod vendor.
Example for Tyk Gateway v5.0.3
The example below shows how to initialise a Golang plugin module for compiling with Tyk Gateway 5.0.3.
mkdir tyk-plugin
cd tyk-plugin
go mod init tyk-plugin
go get github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk@54e1072a6a9918e29606edf6b60def437b273d0a
go mod tidy
go mod vendor
Example for Tyk Gateway versions prior to v4.2
Versions of Tyk Gateway predating v4.2 rely on graphql-go-tools. An alias needs to be configured to associate imports of github.com/TykTechnologies/graphql-go-tools with github.com/jensneuse/graphql-go-tools. To determine the dependency version open the go.mod file in the associated release branch of the Gateway repository. For example, for Tyk Gateway v4.0.3, the dependency version for graphql-go-tools is v1.6.2-0.20220426094453-0cc35471c1ca. This can be found by inspecting the contents of go.mod in the release-4.0.3 branch, particularly the replace statements within.
mkdir tyk-plugin
cd tyk-plugin
go mod init tyk-plugin
go get github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk@6c76e802a29838d058588ff924358706a078d0c5
go mod edit -replace github.com/jensneuse/graphql-go-tools=github.com/TykTechnologies/graphql-go-tools@v1.6.2-0.20220426094453-0cc35471c1ca
go mod tidy
go mod vendor
The commands listed above will create a go.mod file inside your folder and will ensure that the plugin depends on the right Tyk version.
Write the plugin
Let’s create a plugin with very basic functionality:
- We will add a custom header
"Foo: Bar"to a request. - This needs to happen right before the request is passed to an upstream target behind the Tyk API Gateway
Create a file plugin.go with the following content:
package main
import (
"net/http"
)
// AddFooBarHeader adds custom "Foo: Bar" header to the request
func AddFooBarHeader(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
r.Header.Add("Foo", "Bar")
}
func main() {}
We see that the Golang plugin:
- Is a Golang project with a
mainpackage - Has an empty
func main() - Has one exported
func AddFooBarHeaderwhich must have the same method signature astype HandlerFunc func(ResponseWriter, *Request)from the standard"net/http"Golang package
Sync dependencies
Before version 5.1:
go mod tidy
go mod vendor
Running the command above will download the required dependencies from the internet, and ensure that all plugin dependencies are resolved correctly. All dependencies are saved to the vendor folder.
Note
Run this command on initial plugin initialisation, and every time you add a new third-party library in your code.
Building the plugin
A Golang plugin is built as a shared library (.so), using exactly the same Tyk binary as the one to be installed. We provide a Docker image, that we also use internally for building our official binaries.
The steps for building a plugin are as follows:
- Mount your plugin source code directory to the
/plugin-sourcecontainer location. - Specify the docker tag for the target Tyk Gateway version, e.g.
v5.2.1. - Specify the name for your plugin’s shared library file, e.g.
plugin.so.
An example is shown below that builds a plugin named plugin.so, compatible with Gateway version v5.2.1. This mounts the source code from the current directory into the docker container at /plugin-source.
docker pull tykio/tyk-plugin-compiler:v5.2.1
docker run --rm -v `pwd`:/plugin-source \
--platform=linux/amd64 \
tykio/tyk-plugin-compiler:v5.2.1 plugin.so
Plugin compiler arguments
Most of the following arguments are applied only to developer flows. These aid development and testing purposes, and support of these varies across releases, due to changes in the go ecosystem. The latest plugin compiler currently implements the following options:
- plugin_name = plugin.so (example above)
- build_id = optional, provides build uniqueness
- GOOS = optional override of GOOS (add
-e GOOS=linux) - GOARCH = optional override of GOARCH (add
-e GOARCH=amd64)
By default, if build_id is not provided, the gateway will not allow
loading the plugin twice. This is a restriction of the Go plugins
standard library implementation. As long as the builds are made with
unique build ids, the same plugin can be loaded multiple times.
When you provide a unique build id argument, that also enables hot-reload
compatibility of your .so plugin build, so that you would not need to
restart the gateway, only reload it.
- Before 5.1: the plugin would be built in a filesystem path based on build_id.
- Since 5.2.4: the plugin compiler adjusts the go module in use for the plugin.
As the plugins are built with -trimpath, to omit local filesystem path
details and improve plugin compatibility, the plugin compiler relies on
the go module itself to ensure each plugin build is unique. It modifies
the plugin build go.mod file and imports to ensure a unique build.
- plugin package: Warnings
- golang#29525 - plugin: can’t open the same plugin with different names
To compile your plugins to different architectures and operating systems, provide the additional GOOS and GOARCH arguments to the plugin compiler.
docker run --rm -v `pwd`:/plugin-source \
--platform=linux/amd64 \
tykio/tyk-plugin-compiler:v5.2.1 plugin.so $build_id linux arm64
This example command will cross-compile your plugin for a linux/arm64
architecture. It will produce a plugin_v5.2.1_linux_arm64.so.
If you are using the plugin compiler on MacOS, the docker run argument
--platform=linux/amd64 is necessary. The plugin compiler is a
cross-build environment implemented with linux/amd64.
The plugin compiler also supports a set of environment variables being passed:
DEBUG=1: enables debug output from the plugin compiler process.GO_TIDY=1: runs go mod tidy to resolve possible dependency issues.GO_GET=1: invokes go get to retrieve the exact Tyk gateway dependency.
These environment options are only available in the latest gateway and plugin compiler versions. They are unsupported and aid development and testing workflows.
Loading the plugin
For development purposes, we going to load the plugin from local files. For production, you can use bundles to deploy plugins to multiple gateways.
In the API definition find the custom_middleware section and make it look similar to the snippet below. Tyk Dashboard users should use RAW API Editor to access this section.
"custom_middleware": {
"pre": [],
"post_key_auth": [],
"auth_check": {},
"post": [
{
"name": "AddFooBarHeader",
"path": "<path>/plugin.so"
}
],
"driver": "goplugin"
}
Here we have:
"driver"- Set this togoplugin(no value created for this plugin) which says to Tyk that this custom middleware is a Golang native plugin."post"- This is the hook name. We use middleware with hook typepostbecause we want this custom middleware to process the request right before it is passed to the upstream target (we will look at other types later).post.name- is your function name from the Go plugin project.post.path- is the full or relative (to the Tyk binary) path to.sofile with plugin implementation (make sure Tyk has read access to this file)
Also, let’s set fields "use_keyless": true and "target_url": "http://httpbin.org/" - for testing purposes (we need to see what request arrives to our upstream target and httpbin.org is a perfect fit for that).
The API needs to be reloaded after that change (this happens automatically when you save the updated API in the Dashboard).
Now your API with its Golang plugin is ready to process traffic:
curl http://localhost:8181/my_api_name/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip",
"Foo": "Bar",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
We see that the upstream target has received the header "Foo": "Bar" which was added by our custom middleware implemented as a native Golang plugin in Tyk.
Updating the plugin
Loading an updated version of your plugin requires one of the following actions:
- An API reload with a NEW path or file name of your
.sofile with the plugin. You will need to update the API spec section"custom_middleware", specifying a new value for the"path"field of the plugin you need to reload. - Tyk main process reload. This will force a reload of all Golang plugins for all APIs.
If a plugin is loaded as a bundle and you need to update it you will need to update your API spec with a new .zip file name in the "custom_middleware_bundle" field. Make sure the new .zip file is uploaded and available via the bundle HTTP endpoint before you update your API spec.
When upgrading Tyk Gateway
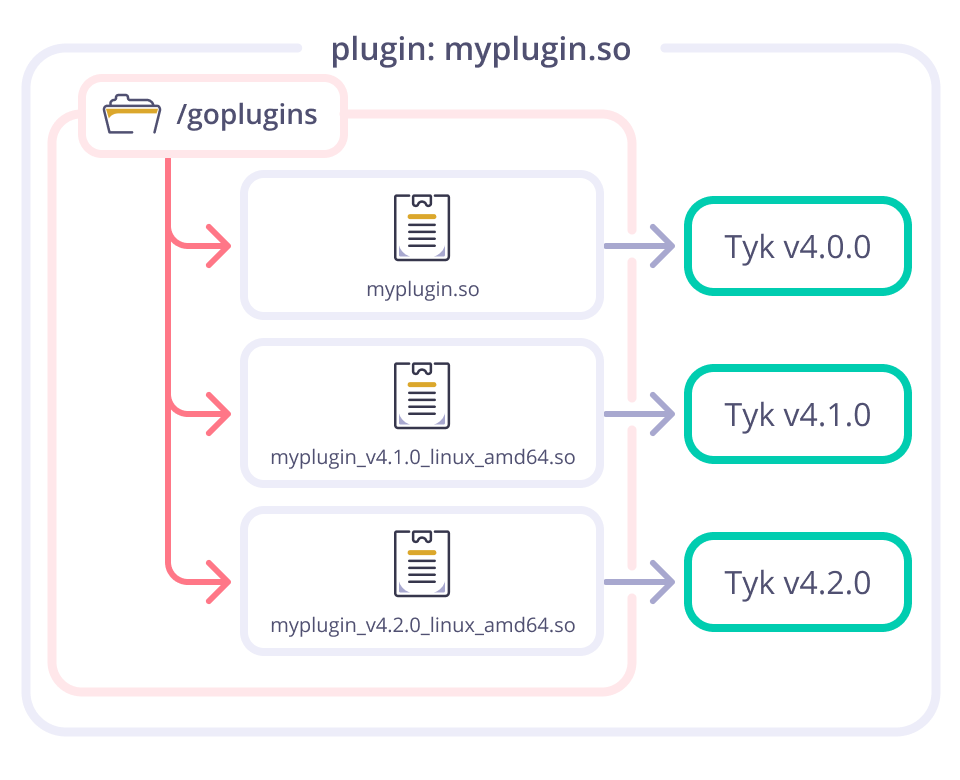
When upgrading your Tyk Gateway deployment, you need to re-compile your plugin with the new version. At the moment of loading a plugin, the Gateway will try to find a plugin with the name provided in the API definition. If none is found then it will fall back to search the plugin file with the name: {plugin-name}_{Gw-version}_{OS}_{arch}.so.
From v4.1.0 the plugin compiler automatically names plugins with the above naming convention. It enables you to have one directory with different versions of the same plugin. For example:
plugin_v4.1.0_linux_amd64.soplugin_v4.2.0_linux_amd64.so
So, if you upgrade from Tyk v4.1.0 to v4.2.0 you only need to have the plugins compiled for v4.2.0 before performing the upgrade.
This diagram shows how every Tyk Gateway will search and load the plugin binary that it is compatible with.
Plugin types
All types of custom middleware hooks are supported by Tyk Golang plugins. They represent different request stages where Golang plugins can be added as part of the middleware chain. Let’s recap the meaning of all these types:
"pre"- contains an array of middlewares to be run before any others (i.e. before authentication)."auth_check"- contains only one middleware info, his middleware performs custom authentication and adds API key session info into the request context."post_key_auth"- contains an array of middlewares to be run after authentication. At this point, we have authenticated the session API key for the given key (in the request context) so we can perform any extra checks."post"- contains an array of middlewares to be run at the very end of the middleware chain, at this point Tyk is about to request a round-trip to the upstream target."response"- run only at the point the response has returned from a service upstream of the API Gateway. NOTE: The method signature for Response Go plugins is slightly different from the other hook types.
Custom Auth Hook
"auth_check" can be used only if both fields in the Tyk API definition are set:
1."use_keyless": false
2."use_go_plugin_auth": true
Post Authentication Hook
"post_key_auth" hook can only be used under the following circumstances:
- When the API is protected, the API spec has a field set as
"use_keyless": false - With any auth method specified in the API definition
Note
These fields are populated automatically with the correct values when you change the authentication method for the API in the Tyk Dashboard.
Examples
Sending HTTP-response from Tyk Golang plugin
It is possible to send a response from the Golang plugin custom middleware. So in the case that the HTTP response was sent:
- The HTTP request processing is stopped and other middleware in the chain won’t be used.
- The HTTP request round-trip to the upstream target won’t happen
- Analytics records will still be created and sent to the analytics processing flow.
Let’s look at an example of how to send an HTTP response from the Tyk Golang plugin. Imagine that we need middleware which would send JSON with the current time if the request contains the parameter get_time=1 in the request query string:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func SendCurrentTime(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// check if we don't need to send reply
if r.URL.Query().Get("get_time") != "1" {
// allow request to be processed and sent to upstream
return
}
//Prepare data to send
replyData := map[string]interface{}{
"current_time": time.Now(),
}
jsonData, err := json.Marshal(replyData)
if err != nil {
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
//Send HTTP response from the Golang plugin
rw.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
rw.Write(jsonData)
}
func main() {}
Let’s build the plugin by running this command in the plugin project folder:
go build -trimpath -buildmode=plugin -o /tmp/SendCurrentTime.so
Then let’s edit the API spec to use this custom middleware:
"custom_middleware": {
"pre": [
{
"name": "SendCurrentTime",
"path": "/tmp/SendCurrentTime.so"
}
],
"post_key_auth": [],
"auth_check": {},
"post": [],
"driver": "goplugin"
}
Let’s check that we still perform a round trip to the upstream target if the request query string parameter get_time is not set:
curl http://localhost:8181/my_api_name/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
Now let’s check if our Golang plugin sends an HTTP 200 response (with JSON containing current time) when we set get_time=1 query string parameter:
curl -v http://localhost:8181/my_api_name/get?get_time=1
* Trying ::1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8181 (#0)
> GET /my_api_name/get?get_time=1 HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8181
> User-Agent: curl/7.54.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Content-Type: application/json
< Date: Wed, 11 Sep 2019 03:44:10 GMT
< Content-Length: 51
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
{"current_time":"2019-09-11T23:44:10.040878-04:00"}
Here we see that:
- We’ve got an HTTP 200 response code.
- The response body has a JSON payload with the current time.
- The upstream target was not reached. Our Tyk Golang plugin served this request and stopped processing after the response was sent.
Authentication with a Golang plugin
You can implement your own authentication method, using a Golang plugin and custom "auth_check" middleware. Ensure you set the two fields in Post Authentication Hook:
Let’s have a look at the code example. Imagine we need to implement a very trivial authentication method when only one key is supported (in the real world you would want to store your keys in some storage or have some more complex logic).
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/ctx"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/headers"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/user"
)
func getSessionByKey(key string) *user.SessionState {
//Here goes our logic to check if the provided API key is valid and appropriate key session can be retrieved
// perform auth (only one token "abc" is allowed)
if key != "abc" {
return nil
}
// return session
return &user.SessionState{
OrgID: "default",
Alias: "abc-session",
}
}
func MyPluginAuthCheck(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
//Try to get a session by API key
key := r.Header.Get(headers.Authorization)
session := getSessionByKey(key)
if session == nil {
// auth failed, reply with 403
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusForbidden)
return
}
// auth was successful, add the session to the request's context so other middleware can use it
ctx.SetSession(r, session, true)
// if compiling on a version older than 4.0.1, use this instead
// ctx.SetSession(r, session, key, true)
}
func main() {}
A couple of notes about this code:
- The package
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/ctx"is used to set a session in the request context - this is something"auth_check"-type custom middleware is responsible for. - The package
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/user"is used to operate with Tyk’s key session structure. - Our Golang plugin sends a 403 HTTP response if authentication fails.
- Our Golang plugin just adds a session to the request context and returns if authentication was successful.
Let’s build the plugin by running the following command in the folder containing your plugin project:
go build -trimpath -buildmode=plugin -o /tmp/MyPluginAuthCheck.so
Now let’s check if our custom authentication works as expected (only one key "abc" should work).
Authentication will fail with the wrong API key:
curl -v -H "Authorization: xyz" http://localhost:8181/my_api_name/get
* Trying ::1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8181 (#0)
> GET /my_api_name/get HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8181
> User-Agent: curl/7.54.0
> Accept: */*
> Authorization: xyz
>
< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
< Date: Wed, 11 Sep 2019 04:31:34 GMT
< Content-Length: 0
<
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
Here we see that our custom middleware replied with a 403 response and request processing was stopped at this point.
Authentication successful with the right API key:
curl -v -H "Authorization: abc" http://localhost:8181/my_api_name/get
* Trying ::1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8181 (#0)
> GET /my_api_name/get HTTP/1.1
> Host: localhost:8181
> User-Agent: curl/7.54.0
> Accept: */*
> Authorization: abc
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: true
< Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
< Content-Type: application/json
< Date: Wed, 11 Sep 2019 04:31:39 GMT
< Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
< Server: nginx
< X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
< X-Frame-Options: DENY
< X-Ratelimit-Limit: 0
< X-Ratelimit-Remaining: 0
< X-Ratelimit-Reset: 0
< X-Xss-Protection: 1; mode=block
< Content-Length: 257
<
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Accept-Encoding": "gzip",
"Authorization": "abc",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0"
},
"url": "https://httpbin.org/get"
}
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
Here we see that our custom middleware successfully authenticated the request and we received a reply from the upstream target.
Logging from a Golang plugin
Your Golang plugin can write log entries as part of Tyk’s logging system.
To do so you just need to import the package "github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/log" and use the exported public method Get():
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/log"
)
var logger = log.Get()
// AddFooBarHeader adds custom "Foo: Bar" header to the request
func AddFooBarHeader(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
logger.Info("Processing HTTP request in Golang plugin!!")
r.Header.Add("Foo", "Bar")
}
func main() {}
Monitoring instrumentation for Tyk Golang plugins
All custom middleware implemented as Golang plugins support Tyk’s current built in instrumentation.
The format for an event name with metadata is: "GoPluginMiddleware:" + Path + ":" + SymbolName, e.g., for our example, the event name will be:
"GoPluginMiddleware:/tmp/AddFooBarHeader.so:AddFooBarHeader"
The format for metric with execution time (in nanoseconds) will have the same format but with the .exec_time suffix:
"GoPluginMiddleware:/tmp/AddFooBarHeader.so:AddFooBarHeader.exec_time"
Accessing the internal state of a Tyk Golang plugin
A Golang plugin can be treated as a normal Golang package but:
- The package name is always
"main"and this package cannot be imported. - This package loads at run-time by Tyk and loads after all other Golang packages.
- This package has to have an empty
func main() {}.
A Golang plugin as a package can have func init() and it gets called only once (when Tyk loads this plugin for the first time for an API).
It is possible to create structures or open connections to 3d party services/storage and then share them within every call and export the function in your Golang plugin.
For example, here is an example of a Tyk Golang plugin with a simple hit counter:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"sync"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/ctx"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/log"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/user"
)
var logger = log.Get()
// plugin exported functionality
func MyProcessRequest(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
endPoint := r.Method + " " + r.URL.Path
logger.Info("Custom middleware, new hit:", endPoint)
hitCounter := recordHit(endPoint)
logger.Debug("New hit counter value:", hitCounter)
if hitCounter > 100 {
logger.Warning("Hit counter to high")
}
reply := myReply{
Session: ctx.GetSession(r),
Endpoint: endPoint,
HitCounter: hitCounter,
}
jsonData, err := json.Marshal(reply)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err.Error())
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
rw.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
rw.Write(jsonData)
}
// called once plugin is loaded, this is where we put all initialisation work for plugin
// i.e. setting exported functions, setting up connection pool to storage and etc.
func init() {
hitCounter = make(map[string]uint64)
}
// plugin internal state and implementation
var (
hitCounter map[string]uint64
hitCounterMu sync.Mutex
)
func recordHit(endpoint string) uint64 {
hitCounterMu.Lock()
defer hitCounterMu.Unlock()
hitCounter[endpoint]++
return hitCounter[endpoint]
}
type myReply struct {
Session *user.SessionState `json:"session"`
Endpoint string `json:"endpoint"`
HitCounter uint64 `json:"hit_counter"`
}
func main() {}
Here we see how the internal state of the Golang plugin is used by the exported function MyProcessRequest (the one we set in the API spec in the "custom_middleware" section). The map hitCounter is used to send internal state and count hits to different endpoints. Then our exported Golang plugin function sends an HTTP reply with endpoint hit statistics.
Loading a Tyk Golang plugin from a bundle
So far we have loaded Golang plugins only directly from the file system. However, when you have multiple gateway instances, you need a more dynamic way to load plugins. Tyk offer bundle instrumentation Plugin Bundles. Using the bundle command creates an archive with your plugin, which you can deploy to the HTTP server (or AWS S3) and then your plugins will be fetched and loaded from that HTTP endpoint.
You will need to set in tyk.conf these two fields:
"enable_bundle_downloader": true- enables the plugin bundles downloader"bundle_base_url": "http://mybundles:8000/abc"- specifies the base URL with the HTTP server where you place your bundles with Golang plugins (this endpoint must be reachable by the gateway)
Also, you will need to specify the following field in your API spec:
"custom_middleware_bundle" - here you place your filename with the bundle (.zip archive) to be fetched from the HTTP endpoint you specified in your tyk.conf parameter "bundle_base_url"
So, your API spec will have this field:
"custom_middleware_bundle": "FooBarBundle.zip"
Let’s look at FooBarBundle.zip contents. It is just a ZIP archive with two files archived inside:
AddFooBarHeader.so- this is our Golang pluginmanifest.json- this is a special file with meta information used by Tyk’s bundle loader
The contents of manifest.json:
{
"file_list": [
"AddFooBarHeader.so"
],
"custom_middleware": {
"post": [
{
"name": "AddFooBarHeader",
"path": "AddFooBarHeader.so"
}
]
},
"driver": "goplugin",
...
}
Here we see:
- field
"custom_middleware"with exactly the same structure we used to specify"custom_middleware"in API spec without bundle - field
"path"in section"post"now contains just a file name without any path. This field specifies.sofilename placed in a ZIP archive with the bundle (remember how we specified"custom_middleware_bundle": "FooBarBundle.zip").
Accessing API definition from a Golang plugin
When Tyk passes a request to your plugin, the API definition is made available as part of the request context. This can be accessed as follows:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/ctx"
)
func main() {}
func MyPluginFunction(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
apidef := ctx.GetDefinition(r)
fmt.Println("API name is", apidef.Name)
}
ctx.GetDefinition returns an APIDefinition object, the Go data structure can be found here
Accessing OAS API definition from a Golang plugin
When Tyk passes a request to your plugin, the OAS API definition is made available as part of the request context. This can be accessed as follows:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/ctx"
)
func main() {}
func MyPluginFunction(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
oas := ctx.GetOASDefinition(r)
fmt.Println("OAS doc title is", oas.Info.Title)
}
ctx.GetOASDefinition returns an OAS object containing the Tyk OAS API definition. The Go data structure can be found here
Warning
ctx.GetDefinition returns nil if called from a Tyk OAS API and ctx.GetOASDefinition returns nil if called from a Tyk Classic API.
Accessing User session from a Golang plugin
When Tyk passes a request to your plugin, the User sesssion object is made available as part of the request context. This can be accessed as follows:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk/ctx"
)
func main() {}
func MyPluginFunction(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
session := ctx.GetSession(r)
fmt.Println("Developer ID:", session.MetaData["tyk_developer_id"]
fmt.Println("Developer Email:", session.MetaData["tyk_developer_email"]
}
ctx.GetSession returns an UserSession object, the Go data structure can be found here
Modifying a response
Now you need to instruct Tyk to load this shared library for an API so it will start processing traffic as part of the middleware chain. To do so you will need to edit your API spec using the raw JSON editor in the Tyk Dashboard or directly in the JSON file (in the case of the Open Source edition). This change needs to be done for the “custom_middleware” field and it looks like this:
"custom_middleware": {
"pre": [],
"post_key_auth": [],
"auth_check": {},
"post": [],
"response": [
{
"name": "MyResponsePlugin",
"path": "<path>/resplugin.so"
}
],
"driver": "goplugin"
}
Here you have:
"driver" - Set this to Goplugin (no value created for this plugin) which says to Tyk that this custom middleware is a Golang native plugin.
"response" - This is the hook name. You use middleware with a hook type response because you want this custom middleware to process the request on its return leg of a round trip.
response.name - is your function name from the go plugin project.
response.path - is the full or relative (to the Tyk binary) path to .so file with plugin implementation (make sure Tyk has read access to this file)
Response plugin method signature
To write a response plugin in Go you need it to have a method signature as in the example below i.e. func MyResponseFunctionName(rw http.ResponseWriter, res *http.Response, req *http.Request). You can then access and modify any part of the request or response. User session and API definition data can be accessed as with other Go plugin hook types.
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/json"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
)
// MyPluginResponse intercepts response from upstream
func MyPluginResponse(rw http.ResponseWriter, res *http.Response, req *http.Request) {
// add a header to our response object
res.Header.Add("X-Response-Added", "resp-added")
// overwrite our response body
var buf bytes.Buffer
buf.Write([]byte(`{"message":"Hi! I'm a response plugin"}`))
res.Body = ioutil.NopCloser(&buf)
}
func main() {}
Golang Virtual Endpoints
As of Tyk v4+, Golang plugins are available for invocation as part of the API Designer middleware chain.
This means that one or many Golang functions can be called on path and method combinations similar to existing JSVM virtual endpoints
Golang virtual endpoints can be either a high-performance replacement for the JSVM virtual endpoints or for cases when you want to utilise external libraries.
In addition, unlike JSVM virtual endpoints which always must be returned from the middleware, we use the existing Golang plugin framework with these Golang virtual endpoints meaning requests can be passed onwards or a response can be sent from the Golang virtual endpoint.
Adding Golang Virtual Endpoints to your API definition
Golang virtual endpoints follow the same layout and setup as other elements in the extended_path section of the API definition. i.e.:
...
"go_plugin: [
{
"plugin_path": "../test/goplugins/goplugins.so",
"path": "/get",
"method": "GET",
"func_name": "MyPluginPerPathFoo"
},
{
"plugin_path": "../test/goplugins/goplugins.so",
"path": "/bar",
"method": "GET",
"func_name": "MyPluginPerPathBar"
}
]
...
The parameters are similar to other endpoint designer middleware.
plugin_pathis the relative path of the shared object containing the function you wish to call. One or many.sofiles can be called.pathis the regex path on the API you want this middleware to be called onmethodis the HTTP method on which this middleware sits alongside its relative pathfunc_nameis the “symbol” or function you are calling in your Golang plugin shared object file once loaded - a function can be called by one or more APIs and is concurrency safe
Responding from Golang virtual endpoints
See https://tyk.io/docs/plugins/supported-languages/golang/#sending-http-response-from-tyk-golang-plugin as Golang virtual endpoints work in the same way but are configured in a different part of the API definition as per the fields defined above. The Goland virtual endpoints run after all other endpoint designer middlewares apart from JSVM virtual endpoints and request signing.
Simple Golang virtual endpoint example
You can follow the existing Golang plugin example above https://tyk.io/docs/plugins/supported-languages/golang/#golang-plugin-example as a starting point and refer to the loading Golang virtual endpoints to your API definition section above to load your Go virtual endpoint plugins.
Building from Source
If you are building a plugin for a Gateway version compiled from the source, you can use the following command:
go build -trimpath -buildmode=plugin -o plugin.so
As a result of this build command, we get a shared library with the plugin implementation placed at plugin.so.
If your plugin depends on third-party libraries, ensure to vendor them, before building. If you are using Go modules, it should be as simple as running go mod vendor command.
Known Issues and Limitations
If a dependency that your plugin uses is also used by the gateway, the version used by the gateway will be used in your plugin. This may mask conflicts between transitive dependencies.
The plugin compiler is not supported on Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) as it uses glibc 2.23 which is incompatible with our standard build environment. If you absolutely must have Goplugin support on Xenial, please write to our support.
Tyk Cloud Platform
The following supporting resources are available for developing plugins on Tyk Cloud platform: