Dashboard on Red Hat (RHEL) / CentOS
Last updated: 6 minutes read.
Requirements
Ansible is required to run the following commands. Instructions on how install Tyk Dashboard with shell is in the Shell tab.
Getting Started
- clone the tyk-ansible repository
$ git clone https://github.com/TykTechnologies/tyk-ansible
cdinto the directory
$ cd tyk-ansible
- Run initialisation script to initialise environment
$ sh scripts/init.sh
-
Modify
hosts.ymlfile to update ssh variables to your server(s). You can learn more about the hosts file here -
Run ansible-playbook to install
tyk-dashboard
$ ansible-playbook playbook.yaml -t tyk-dashboard
Supported Distributions
| Distribution | Version | Supported |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon Linux | 2 | ✅ |
| CentOS | 8 | ✅ |
| CentOS | 7 | ✅ |
| RHEL | 8 | ✅ |
| RHEL | 7 | ✅ |
Variables
vars/tyk.yaml
| Variable | Default | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| secrets.APISecret | 352d20ee67be67f6340b4c0605b044b7 |
API secret |
| secrets.AdminSecret | 12345 |
Admin secret |
| dash.license | Dashboard license | |
| dash.service.host | Dashboard server host if different than the hosts url | |
| dash.service.port | 3000 |
Dashboard server listening port |
| dash.service.proto | http |
Dashboard server protocol |
| dash.service.tls | false |
Set to true to enable SSL connections |
Install Tyk Dashboard on Red Hat
Tyk has its own signed RPMs in a YUM repository hosted by the kind folks at packagecloud.io, which makes it easy, safe and secure to install a trusted distribution of the Tyk Gateway stack.
This configuration should also work (with some tweaks) for CentOS.
Prerequisites
- Ensure port
3000is open: This is used by the Dashboard to provide the GUI and the Classic Developer Portal. - Follow the steps provided in this link Getting started on Red Hat (RHEL / CentOS) to install and configure Tyk dependencies.
Step 1: Set up YUM Repositories
First, install two package management utilities yum-utils and a file downloading tool wget:
sudo yum install yum-utils wget
Then install Python:
sudo yum install python3
Step 2: Configure and Install the Tyk Dashboard
Create a file named /etc/yum.repos.d/tyk_tyk-dashboard.repo that contains the repository configuration settings for YUM repositories tyk_tyk-dashboard and tyk_tyk-dashboard-source used to download packages from the specified URLs, including GPG key verification and SSL settings, on a Linux system.
Make sure to replace el and 8 in the config below with your Linux distribution and version:
[tyk_tyk-dashboard]
name=tyk_tyk-dashboard
baseurl=https://packagecloud.io/tyk/tyk-dashboard/el/8/$basearch
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://packagecloud.io/tyk/tyk-dashboard/gpgkey
sslverify=1
sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
metadata_expire=300
[tyk_tyk-dashboard-source]
name=tyk_tyk-dashboard-source
baseurl=https://packagecloud.io/tyk/tyk-dashboard/el/8/SRPMS
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://packagecloud.io/tyk/tyk-dashboard/gpgkey
sslverify=1
sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
metadata_expire=300
We’ll need to update the YUM package manager’s local cache, enabling only the tyk_tyk-dashboard repository while disabling all other repositories --disablerepo='*' --enablerepo='tyk_tyk-dashboard', and confirm all prompts -y.
sudo yum -q makecache -y --disablerepo='*' --enablerepo='tyk_tyk-dashboard'
Install Tyk dashboard:
sudo yum install -y tyk-dashboard
Step 3: Confirm Redis and MongoDB or PostgreSQL are running
Start Redis since it is always required by the Dashboard.
sudo service redis start
Then start either MongoDB or PostgreSQL depending on which one you are using.
sudo systemctl start mongod
sudo systemctl start postgresql-13
Step 4: Configure Tyk Dashboard
We can set the Dashboard up with a similar setup command, the script below will get the Dashboard set up for the local instance. Make sure to use the actual DNS hostname or the public IP of your instance as the last parameter.
sudo /opt/tyk-dashboard/install/setup.sh --listenport=3000 --redishost=<Redis Hostname> --redisport=6379 --mongo=mongodb://<Mongo IP Address>:<Mongo Port>/tyk_analytics --tyk_api_hostname=$HOSTNAME --tyk_node_hostname=http://localhost --tyk_node_port=8080 --portal_root=/portal --domain="XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX"
Replace <Redis Hostname>, <Mongo IP Address> and <Mongo Port> with your own values to run this script.
sudo /opt/tyk-dashboard/install/setup.sh --listenport=3000 --redishost=<Redis Hostname> --redisport=6379 --storage=postgres --connection_string=postgresql://<User>:<Password>@<PostgreSQL Hostname>:<PostgreSQL Port>/<PostgreSQL DB> --tyk_api_hostname=$HOSTNAME --tyk_node_hostname=http://localhost --tyk_node_port=8080 --portal_root=/portal --domain="XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX"
Replace <Redis Hostname>,<PostgreSQL Hostname>,<PostgreSQL Port>, <PostgreSQL User>, <PostgreSQL Password> and <PostgreSQL DB> with your own values to run the script.
With these values your are configuring the following:
--listenport=3000: Tyk Dashboard (and Portal) to listen on port3000.--redishost=<hostname>: Tyk Dashboard should use the local Redis instance.--redisport=6379: The Tyk Dashboard should use the default port.--domain="XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX": Bind the Dashboard to the IP or DNS hostname of this instance (required).--mongo=mongodb://<Mongo IP Address>:<Mongo Port>/tyk_analytics: Use the local MongoDB (should always be the same as the Gateway).--storage=postgres: In case, your preferred storage Database is PostgreSQL, use storage type “postgres” and specify connection string.--connection_string=postgresql://<User>:<Password>@<PostgreSQL Host Name>:<PostgreSQL Port>/<PostgreSQL DB>: Use the PostgreSQL instance provided in the connection string (should always be the same as the gateway).--tyk_api_hostname=$HOSTNAME: The Tyk Dashboard has no idea what hostname has been given to Tyk, so we need to tell it, in this instance we are just using the local HOSTNAME env variable, but you could set this to the public-hostname/IP of the instance.--tyk_node_hostname=http://localhost: The Tyk Dashboard needs to see a Tyk node in order to create new tokens, so we need to tell it where we can find one, in this case, use the one installed locally.--tyk_node_port=8080: Tell the Dashboard that the Tyk node it should communicate with is on port 8080.--portal_root=/portal: We want the Portal to be shown on /portal of whichever domain we set for the Portal.
Step 5: Start Tyk Dashboard
sudo service tyk-dashboard start
Note
To check the logs from the deployment run:
sudo journalctl -u tyk-dashboard
Notice how we haven’t actually started the gateway yet, because this is a Dashboard install, we need to enter a license first.
Note
When using PostgreSQL you may receive the error: "failed SASL auth (FATAL: password authentication failed for user...)", follow these steps to address the issue:
- Open the terminal or command prompt on your PostgreSQL server.
- Navigate to the location of the
pg_hba.conffile. This file is typically located at/var/lib/pgsql/13/data/pg_hba.conf. - Open the
pg_hba.conffile using a text manipulation tool. - In the
pg_hba.conffile, locate the entry corresponding to the user encountering the authentication error. This entry might resemble the following:
host all all <IP_address>/<netmask> scram-sha-256
- In the entry, find the METHOD column. It currently has the value scram-sha-256.
- Replace scram-sha-256 with md5, so the modified entry looks like this:
host all all <IP_address>/<netmask> md5
- Save the changes you made to the
pg_hba.conffile. - Restart the PostgreSQL service to apply the modifications:
sudo systemctl restart postgresql-13
Step 6: Enter Dashboard license
Add your license in /var/opt/tyk-dashboard/tyk_analytics.conf in the license field.
If all is going well, you will be taken to a Dashboard setup screen - we’ll get to that soon.
Step 7: Restart the Dashboard process
Because we’ve just entered a license via the UI, we need to make sure that these changes get picked up, so to make sure things run smoothly, we restart the Dashboard process (you only need to do this once) and (if you have it installed) then start the gateway:
sudo service tyk-dashboard restart
Step 8 - Go to the Tyk Dashboard URL
Go to the following URL to access to the Tyk Dashboard:
127.0.0.1:3000
You should get to the Tyk Dashboard Setup screen:
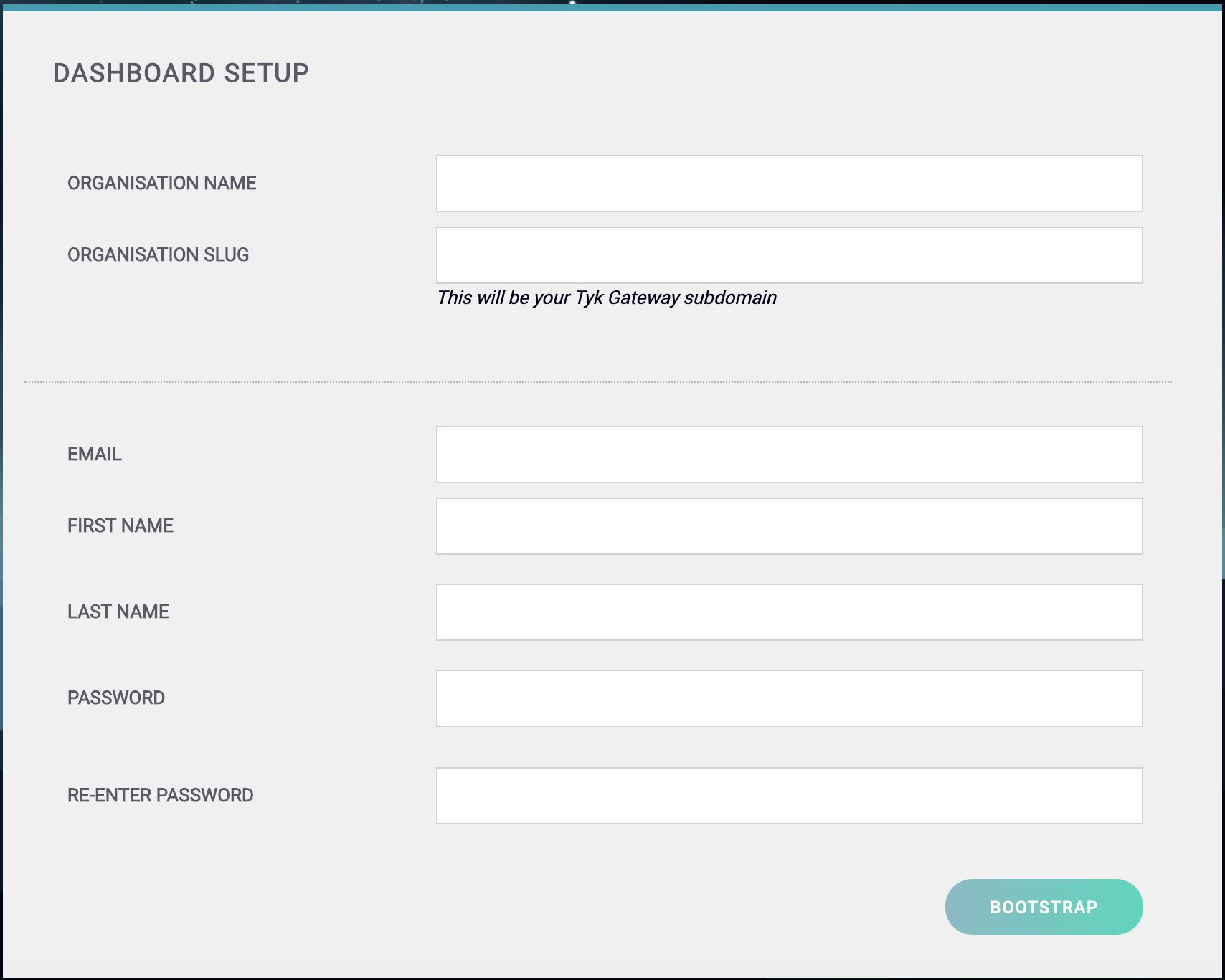
Step 9 - Create your Organisation and Default User
You need to enter the following:
- Your Organisation Name
- Your Organisation Slug
- Your User Email Address
- Your User First and Last Name
- A Password for your User
- Re-enter your user Password
Note
For a password, we recommend a combination of alphanumeric characters, with both upper and lower case letters.
Click Bootstrap to save the details.
Step 10 - Login to the Dashboard
You can now log in to the Tyk Dashboard from 127.0.0.1:3000, using the username and password created in the Dashboard Setup screen.
Configure your Developer Portal
To set up your Developer Portal follow our Self-Managed tutorial on publishing an API to the Portal Catalogue.